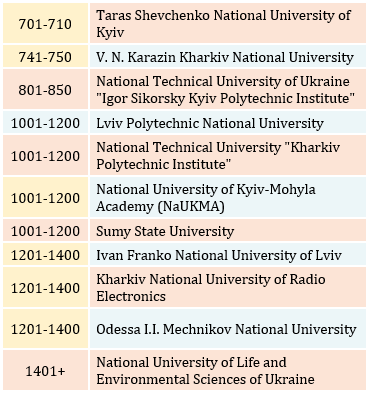
NURE positions in the QS World University Rankings (QS University World Rankings tab)
QS World University Rankings is considered one of the most influential global rankings of universities. Developed in 2004 by Quacquarelli Symonds in conjunction with the British edition of Times Higher Education. Until 2010, it was known as The World University Rankings. Since 2010, the single rating has been split into two:
- Times Higher Education publishes a ranking of the world’s top universities, The World Reputation Rankings, in conjunction with Thomson Reuters;
- Quacquarelli Symonds continues to issue a rating called QS World University Rankings.
The universities rate the rating according to the following indicators:
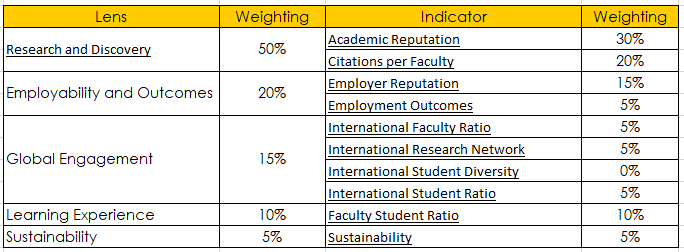
These indicators cover the key strategic missions of universities of global importance, for which they are responsible to the participants of the process: the academic community, employers, students and their parents. More than 2,500 higher education institutions around the world are evaluated annually. According to its results, the ranking of the top 500 universities in the world and the rankings of universities by individual disciplines.
QS Global Academic Survey includes professors and university leaders with an average of 19.6 years of experience in science. Leading scientists and rectors of more than 500 universities are among them. A respondent may name up to 30 universities without naming the university they serve. The survey was conducted in five subjects: natural sciences, social sciences, humanities and arts, life sciences, engineering sciences, and technologies. Several thousand companies from more than 90 countries take part in the QS Global Employer Survey.
The level of university achievement is evaluated based on the results of a combination of statistical analysis of educational institutions, audited data (including citation index information from the Scopus database of the world’s largest bibliographic database of scientific publications), as well as data from a global expert survey of representatives of the international academic society and employers who express their thoughts about universities.
In 2022, the Kharkiv National University of Radio Electronics was included in the ranking for the first time.
In total, the ranking includes 11 Ukrainian universities: